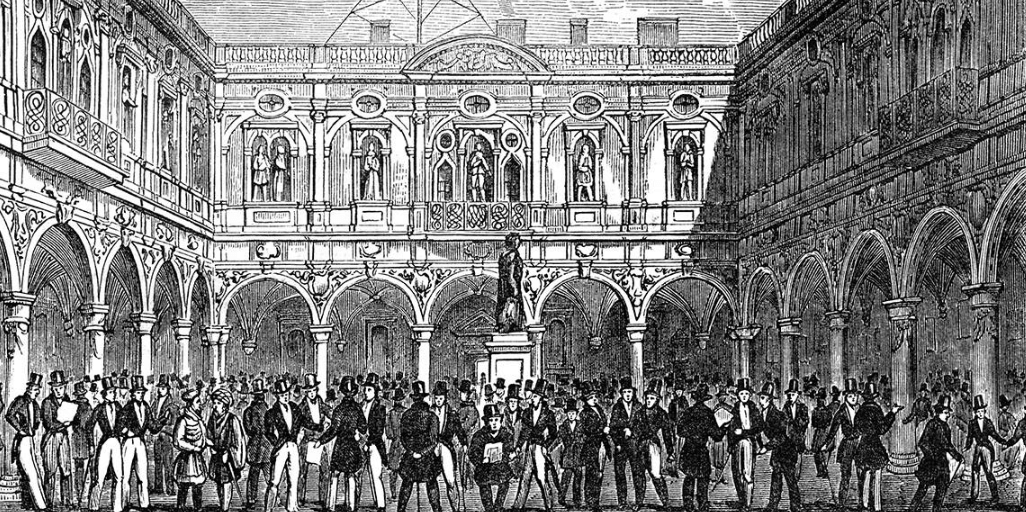
Do you need to quickly build a web UI for your smart contracts?
Etherscan can do that for you! Read on to learn how to verify your Solidity smart contracts on Etherscan.
Continue reading →
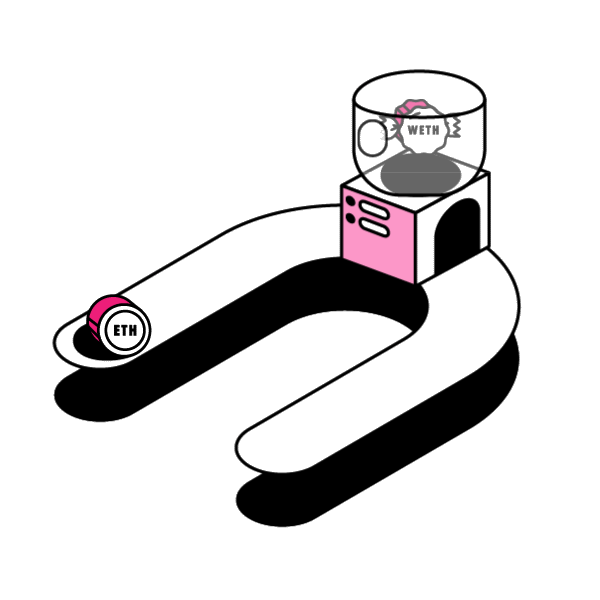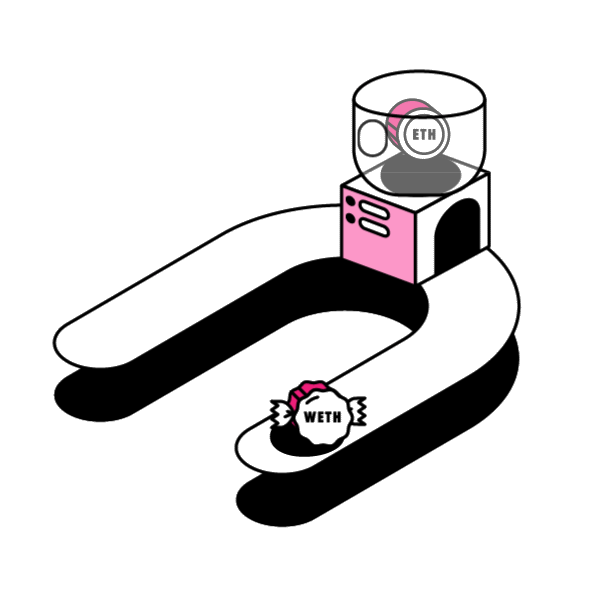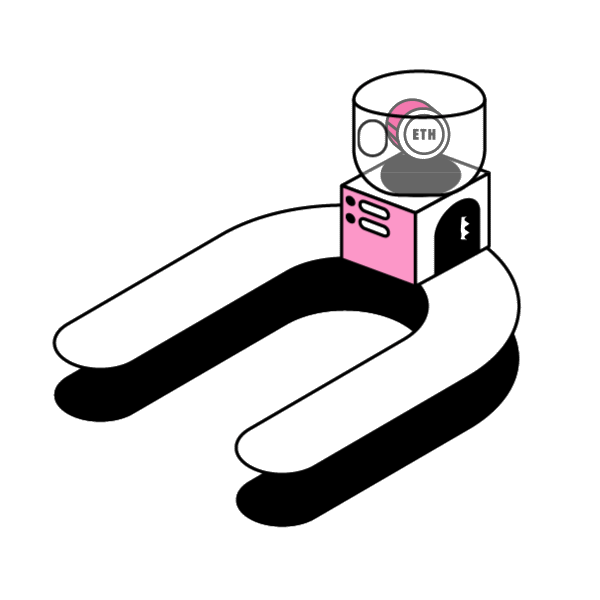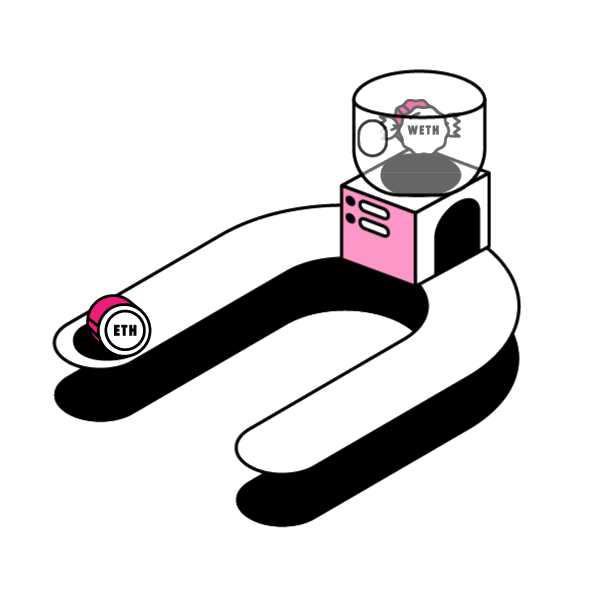
Smart contracts’ open source and immutable nature enables permissionless innovation in the space. People and companies can innovate on top of protocols without worrying about the rules of the game changing later on. Any Developer can innovate and build new dApps freely in a permissionless manner, without needing anybody’s approval.
When a dApp (decentralized app) is built off of the Ethereum Blockchain it usually implements its own ERC20 Token. Think Augur’s REP Token, or Bancor’s BNT Token. ERC20 is a token standard developed after the release of ETH that defines how tokens are transferred and how to keep a consistent record of those transfers among tokens in the Ethereum Network.
Decentralized services can be composed together to harness their particular strengths. The question is: How can developers extend the capability of an existing ERC20 token contract? In this article, let’s examine a design pattern around smart contract extensibility: Wrapped Tokens.
Continue reading →

I won the Singapore National Blockchain Challenge. Read on to learn more about my winning project around decentralized crowdfunding.
Platforms such as Patreon has high fees and can deplatform you at any time. Instead of having to go through a centralized platform, what if Creators can utilize smart contracts and decentralized protocols to crowdfund in an intermediary-free way?
Enter Patronage Collectibles.
You can check out our post-hackathon interview here.
Continue reading →
To learn more about the why, check out The Fall of Fan Patronage.
A Patronage Market is a cryptoeconomic system that facilitates the creation of market-driven communities between Creators and Patrons on the Ethereum blockchain, without the need to trust counterparties or to pass intermediaries. It’s an alternative crowdfunding mechanism for a creative space plagued by platform censorship.
In a Patronage Market:
- Creators issue unique personal cryptocurrencies backed by products and/or services which makes it spendable.
- Patrons collect tokens to redeem it for services and/or exclusive privileges, acquire social status, and invest in promising Creators.
The market uses a ‘complementary currency’ called Patronage Tokens as the currency of exchange, creating tokenized economies and communities.
Let’s learn about the Patronage Markets concept and how it works.
Continue reading →
In recent years, alternative ways to raise capital has risen in popularity.
Crowdfunding lets projects to be funded by raising small amounts of money from a large number of backers.
Subscription patronage lets fans support their favourite Creators with regular payments in exchange for goods or special perks. Both crowdfunding and subscription patronage has helped creators reduce risk and generate a reliable income from their work. Lots of interesting projects would not have been possible without them.
However, deplatforming has become a major risk to fan funding. Large tech companies can and have deplatformed and demonetized many independent creators with little explanation or notice. This phenomena effectively destroys creators’ audience and income should it happen to them.
Continue reading →

Most people who got into in cryptocurrencies saw it primarily for its potential for financial gain. Tokens were an accessible asset class that anybody could purchase without being a ‘proper’ investor.
After an unprecedented boom in 2017, the price of bitcoin fell by about 65 percent after January 2018. By September 2018, cryptocurrencies collapsed 80% from their peak in January 2018. We are currently experiencing the longest bear market - a ‘crypto winter’ - in the brief and turbulent history of cryptocurrency.
However, speculative bubbles around a disruptive technology are nothing new.
Continue reading →

Cryptocollectibles are rapidly becoming one of the earliest mainstream use cases of the blockchain. Let’s examine how the blockchain is changing how we view art.
Continue reading →
The ERC20 token standard has achieved near-complete industry adoption. It defined six minimal requirements for the way tokens behave on the Ethereum blockchain. Anyone could comply with the token standard and implement additional functions as needed. This standard ignited the ICO wave, allowing for the creation of core infrastructure and exchanges that is the backbone of the crypto ecosystem today.
Let’s look at Ethereum ERC standards you should know about - including some you’ve never seen before!
Continue reading →

Relying on meme magic to support a token value is a risky idea. While attractive because of its ability to raise capital, these tokens will find themselves at risk of collapse when the market turns.
For a token to have a stable value, it needs token sinks - places where tokens can be ‘spent’ so the total circulating supply decreases over time. In this article, we’ll examine several real-life token projects and how they make their tokens spendable. We’ll look at three token models: Protocol Tokens, Platform Tokens, and Governance Tokens.
Continue reading →

In the Harberger Taxes is an economic abstraction that aims to democratize the control of assets between private and commons ownership. In this taxation system, asset owners self-assess the value of assets they own and pay a tax rate of X% on that value. Whatever value owners specify for the asset, they have to be willing to part ways and sell it to anyone at that price.
💡 Harberger Taxes was repopularized by Radical Markets.
The emerging field of cryptoeconomics uses both cryptography and economic incentives to design decentralized applications. Smart contracts defines the rules of an economic game which incentivize rational actors to behave in optimally desirable ways.
Previously, it was difficult or even impossible for economists to test these ideas in a real environment. Blockchains offer a testing ground for economic abstractions such as Harberger Taxes, where rules can be enforced with smart contracts.
Let’s examine the Harberger Tax model and discover how we can use it in decentralized applications.
Continue reading →